Content

HighRadius Collections Software automates and optimizes the credit & collections management process to improve collector efficiency, minimize bad debt write-offs, improve customer relationships, and reduce DSO. The result is a more efficient collections team that contributes to enhanced cash flow and reduced DSO. On the other hand, allowance for doubtful accounts is an estimation of the AR that a business expects to go unpaid. It is deducted from the total AR of a company even before a customer defaults. Sometimes the collections team might do an excellent job, and bad debt will be much lower, while at other times, it could be a lot higher. Allowance for doubtful accounts falls under the contra assets section of a company’s balance sheet.
- Since it is an estimate of the bad debt expense a company expects to incur, days sales outstanding also plays a vital role in its calculation.
- Sales and the ultimate decision that specific accounts receivable will never be collected can happen months apart.
- Without crediting the Accounts Receivable control account, the allowance account lets the company show that some of its accounts receivable are probably uncollectible.
- A contra-asset account that reduces accounts receivable to the amount that is expected to be collected in cash.
- Companies turn to the allowance method to properly report revenues and the related expenses in the periods that they were earned and incurred.
While most sponsors https://personal-accounting.org/ invoices reliably, occasionally a sponsor is unable to fund the award they made to the University. The third method takes the most granular approach yet by assigning personalized default risk percentages to each customer based on historical trends. This method is commonly used when client relationships span years and provide plenty of historical data for your business to pull from. This means that when it is subtracted from Accounts Receivable, the difference represents an estimate of the cash value of accounts receivable. As you’ve learned above, the delayed recognition of bad debt violates GAAP, specifically the matching principle. Therefore, the direct write-off method is not used for publicly listed companies; the allowance method is used instead. When future collection of receivables cannot be reasonably assumed, recognising this potential nonpayment is required.
Accountabilities
Any subsequent write-offs of accounts receivable against the allowance for doubtful accounts only impact the balance sheet. Most B2B businesses operate by extending trade credit to their customers for a fixed time period. Customers who don’t pay on time are categorized as doubtful accounts asunder. Among these doubtful accounts, some make the payment after multiple follow-ups, and some do not pay at all. So, bad debt expense is the accounts receivable that a business fails to recover from such accounts. Here the business assesses its past records and chooses an appropriate percentage of AR they expect to go unpaid. Since the estimate is made by taking historical data into account, it gives a very close idea of the bad debt a business might incur.
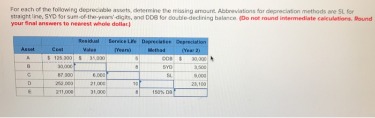
The matching principle states that Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts and expenses must be recorded in the same period in which they occur. Therefore, the allowance is created mainly so the expense can be recorded in the same period revenue is earned. Management may disclose its method of estimating the allowance for doubtful accounts in its notes to the financial statements. Some companies may classify different types of debt or different types of vendors using risk classifications. For example, a start-up customer may be considered a high risk, while an established, long-tenured customer may be a low risk.
Estimation by Historical Percentage
If you use double-entry accounting, you also record the amount of money customers owe you. To protect your business, you can create an allowance for doubtful accounts. Note that some authors and companies may refer to the allowance account as Allowance for Uncollectible Expense, Allowance for Bad Debts or Provision for Bad Debts.
We do not record any estimates or use the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts under the direct write-off method. We record Bad Debt Expense for the amount we determine will not be paid. This method violates the GAAP matching principle of revenues and expenses recorded in the same period. A reserve for doubtful debts can not only help offset the loss you incur from bad debts, but it also can give you valuable insight over time. For example, your ADA could show you how effectively your company is managing credit it extends to customers. It can also show you where you may need to make necessary adjustments (e.g., change who you extend credit to).
How to calculate the allowance for doubtful accounts?
Given that the default probability is unique to each company, this method offers the most accurate way of predicting ADA. However, it’s dependent on maintaining a small, consistent customer base that can be measured, with calculation efforts increasing as your client base grows. Typically, larger businesses rely on one of the first two methods due to the complexity of running these assessments across a big customer pool.
- In addition, the calculations may provide an “early warning” sign of potential problems in receivables management and rising bad debt risks.
- There are several possible ways to estimate the allowance for doubtful accounts, which are noted below.
- The other part of this adjusting entry will be a debit of $900 to Bad Debts Expense.
- This approach looks at the balance of accounts receivable at the end of the period and assumes that a certain amount will not be collected.
Thus, the company cannot enter credits in either the Accounts Receivable control account or the customers’ accounts receivable subsidiary ledger accounts. If only one or the other were credited, the Accounts Receivable control account balance would not agree with the total of the balances in the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger. Without crediting the Accounts Receivable control account, the allowance account lets the company show that some of its accounts receivable are probably uncollectible. For example, assume Rankin’s allowance account had a $300 credit balance before adjustment. However, the balance sheet would show $100,000 accounts receivable less a $5,300 allowance for doubtful accounts, resulting in net receivables of $ 94,700. On the income statement, Bad Debt Expense would still be 1%of total net sales, or $5,000.
Collection agencies should not retain accounts more than twelve months unless there is evidence that collection is imminent. Whenever an invoice is written off as uncollectible, a record of the debt and of the administrative action will be maintained per the UC Records Retention schedule. A receivable account is deemed uncollectible when it remains unpaid after the University has taken all adequate and reasonable efforts to collect an amount due.
AKSO HEALTH : AND SUBSIDIARIES UNAUDITED CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS - Form 6-K - Marketscreener.com
AKSO HEALTH : AND SUBSIDIARIES UNAUDITED CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS - Form 6-K.
Posted: Thu, 16 Feb 2023 11:09:22 GMT [source]
All outstanding accounts receivable are grouped by age, and specific percentages are applied to each group. The aggregate of all group results is the estimated uncollectible amount. Some amounts that have been turned over to collection, or written off, are actually collected, less any collection fees.
What to do with the balance in Allowance for Doubtful Accounts?
To reverse the account, debit your Accounts Receivable account and credit your Allowance for Doubtful Accounts for the amount paid. When it comes to bad debt and ADA, there are a few scenarios you may need to record in your books. In year 4, the ABC Company should use 1.6 percent as its bad debt allowance. Because you can't know in advance the amount of bad debt you'll incur, learn how to make an allowance for potential debts.
Is uncollectible account an expense?
Uncollectible accounts expense is the charge made to the books when a customer defaults on a payment. This expense can be recognized when it is certain that a customer will not pay.
Auditors use several techniques to assess whether the allowance for doubtful accounts appears reasonable. Management can use similar techniques to self-audit the company’s allowance. At the discretion of Campus Billing and Collections, written-off accounts over $10 will be assigned to an outside collection agency for collection when efforts by campus collectors have proven unsuccessful.